IT and cybersecurity have an intricate and nuanced relationship. Understanding how these two spaces work together in a business context is critical to building operations that are intuitive, responsibly automated, scalable, and secure.
By looking at IT vs cybersecurity we can build an understanding of the differences and see how they work together to protect your network.
The difference between IT and cybersecurity is sometimes hard to conceptualize because the two fields have so much in common and they overlap in their purpose: protecting sensitive data and information while blocking out unauthorized personnel.
One way to look at IT vs cybersecurity is that cybersecurity lives on top of IT security. Take a bank, for example, think about the main vault as IT security and the security deposit boxes and alarm systems as cybersecurity.
While the vault, security deposit boxes, and alarm systems are all designed for security, they all serve different functions. The vault acts as the foundation on which additional measures like the security cameras, alarm systems, and safety deposit boxes live.
“We are like islands in the sea, separate on the surface but connected in the deep.”
– William James –
Keep this idea of the vault and the alarms in mind as we further explore the nature of IT and cybersecurity and how they differ from one another.
For more on this topic, listen to experts from Impact and our partner DOT Security in this deep dive webinar, The Difference Between IT vs Cybersecurity Standards exploring how the two fields relate and work together.
The Differences Between IT and Cybersecurity
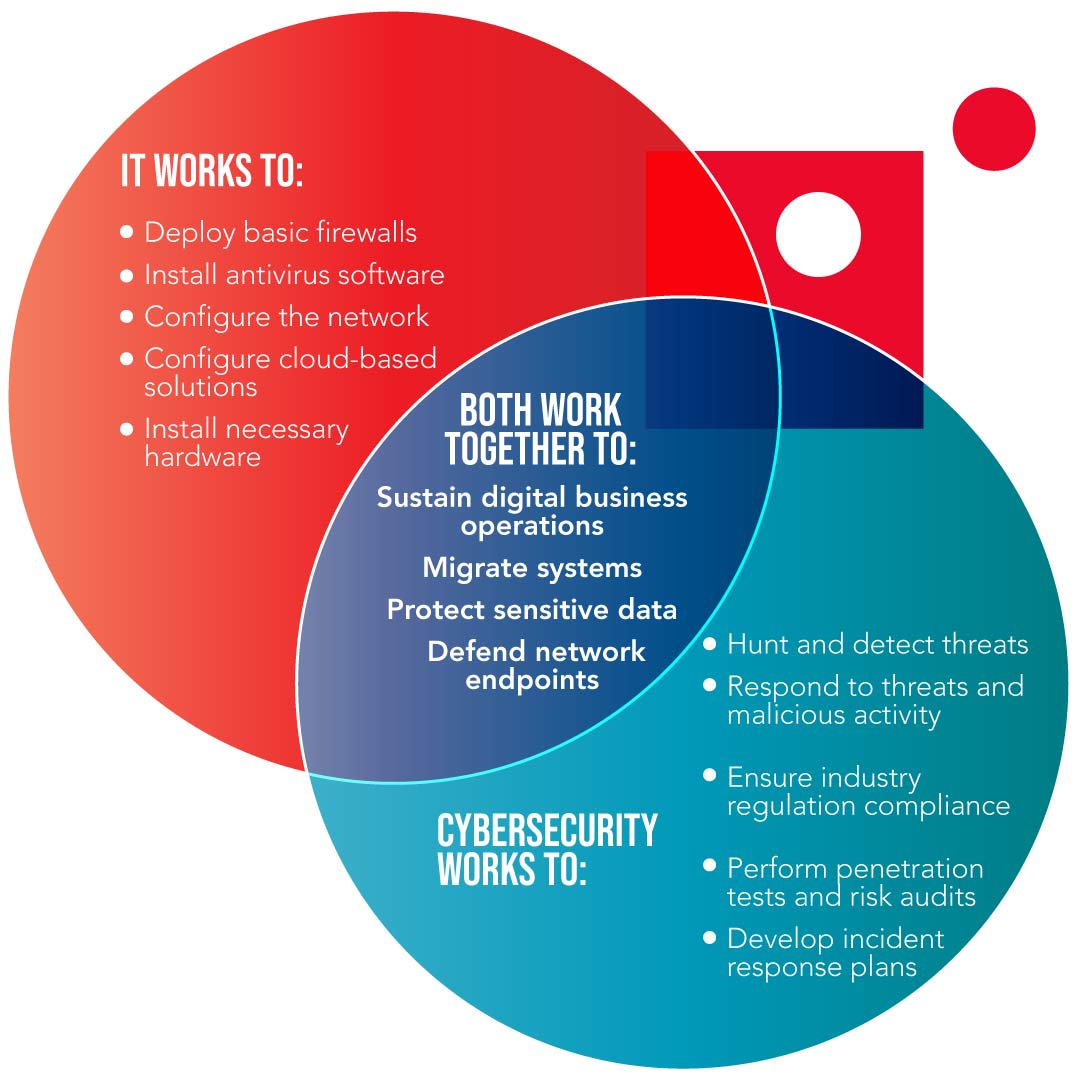
There are several ways to distinguish IT security from cybersecurity. One of the easiest is to consider IT security practices the foundation on which cybersecurity practices are built.
In practice, this means IT security handles certain standard security practices that work to protect the network on a first-defense basis. IT security includes setting up firewalls, installing next-gen antivirus software, using multi-factor-authentication (MFA), configuring the network properly, configuring cloud services, and installing and maintaining physical hardware like servers.
All of this is essential in protecting your network and the various pools of sensitive information housed there. Putting up these first walls of defense also allows you to upgrade your security efforts by fortifying your network with cybersecurity services.
While IT security is critical, it’s far from impenetrable and is more passive than its cybersecurity counterpart. Where IT security is mostly designed to keep malicious users out, cybersecurity specifically aims to identify threats before they strike, find malicious or suspicious activity on the network, minimize the duration of an attack, and minimize the total damage of an attack.
To define this further, cybersecurity is responsible for:
- Threat hunting and detection: Through 24/7 network security monitoring with detection and response, cybersecurity professionals are able to identify and neutralize threats quickly and efficiently.
- Threat response: After calling out a threat, cybersecurity teams actively respond through a variety of proactive defense tactics that work to isolate and eliminate attacks or malicious activity.
- Industry compliance: More and more industries are adopting some sort of standardized approach to cybersecurity practices. The efforts to standardize cybersecurity are aimed at protecting sensitive consumer information.
- Risk audits and penetration testing: Risk audits and penetration testing are used by cybersecurity professionals to identify gaps and weak points in the existing network. This gives a cybersecurity team a really strong overview of the networks security as it stands, and provides insight into how it should be properly fortified.
- Incident response plans: Incident response plans are often designed by a vCISO (virtual Chief Information Security Officer). It’s a plan of action to employ in the event of a specific but hypothetical cyberattack situation. By covering something like a ransomware attack through an incident response plan with your vCISO, you’ll be better prepared in case of an actual attack.
This should demonstrate how cybersecurity practices live on top of and enhance IT security measures in a complimentary way.