In the business world, technology is constantly advancing. As such, it’s important for business leaders and decision-makers to stay on top of the current evolutions, newest solutions, and modern trends to stay up-to-date operationally.
In that vein, blockchain technology has been all the rave as of late, especially in the booming era of cryptocurrency. With that in mind, we’ve put together this guide on how businesses are already using blockchain technology, and what it means for their operations.
Your business is unique, and it needs a unique IT system to handle your specific needs. Learn how Impact can help you customize your IT in our webinar, A Closer Look at Impact’s Approach to Managed IT.
What Is a Blockchain?
A blockchain is an electronic database or ledger that is shared and then verified by the nodes—or connection points—of a computer network. A blockchain gets its name from the “blocks” or datasets that are created whenever a transaction occurs.
To better understand blockchain technology, picture a bank teller writing down each transaction they processed on a piece of paper, then grouping a set of papers into a bigger “block” of data. Finally, the teller would share this data with a massive amount of people and each person would verify the transaction.
Blockchain is secure and decentralized because each transaction is given a timestamp and verified by the network. Therefore, there is no need to have a third party such as a bank keeping track of the transactions.
It is used as the main storage form for cryptocurrencies because it can maintain a secure, decentralized transaction record for purchasing. How it works is, as data comes in to be saved, it is entered into a new block, then it chains itself to the last block, saving in chronological order.
It works so well for cryptocurrencies specifically because decentralized blockchains are immutable, meaning the data entered is irreversible and provides a permanently recorded record of transactions.
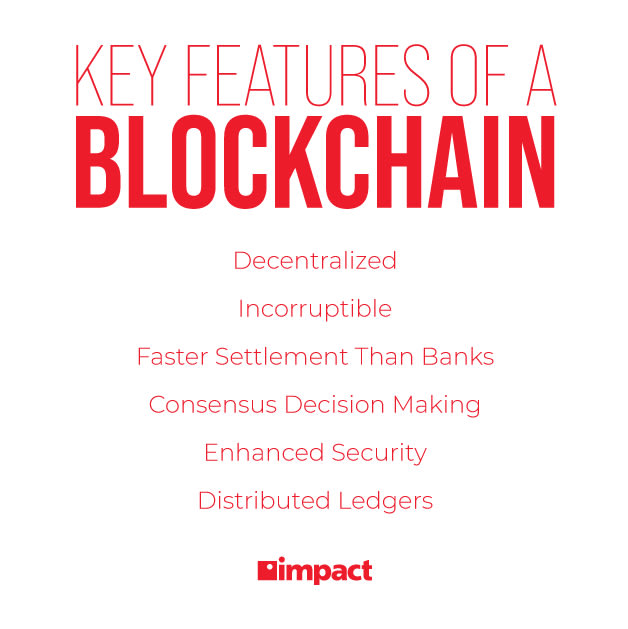
Key Elements and Features of Blockchain
What makes the blockchain so effective? These key elements work together to make it a secure way to record and store digital data:
- Decentralization: A decentralized network means no governing body or third party looking over it.
- Immutable Records: Records stored via blockchain are immutable (incorruptible and unalterable). Blocks on the chain cannot be changed or updated and to add more, every node on the chain must check for validity.
- Greater Security: Blockchains utilize cryptography to protect data using a complex algorithm that acts as a defense against attacks.
- Faster Settlement: Blockchain tech makes transactional periods much quicker than traditional banking systems which can take days to process information. Blockchain makes transactions over long distances faster, easier, and more secure.
- Distributed Ledgers: Distributed ledger technology allows for simultaneous access, validation, and updating of records in an immutable manner across a network that is broken up across multiple entities. This is a core component of blockchain technology because it makes it possible to secure a decentralized digital transaction database. Having networks distributed removes the need for a third party to check for authenticity and manipulation.
Blockchain Applications for Businesses
Now that we have an understanding of what blockchain technology is, and its core elements, we can start to explore the business use cases for this fairly new-aged technology. From automating decision making, to secure data sharing, there are several innovative ways in which modern companies are using blockchain.
Sending and Receiving Payment
One of the most common uses of the blockchain is as a public ledger for cryptocurrencies. Cryptocurrencies are run on blockchain and are a decentralized type of currency since they are verified in a peer-to-peer network. They are not stored by one single entity or bank.
Fast-food restaurants such as Subway and Burger King have begun accepting cryptocurrencies as payment in their European stores. While the cryptocurrency market fluctuates often, many believe this form of currency will be more widespread in the future.
Sharing Records Securely
Businesses can more securely store and transfer records using blockchain networks with strong, built-in encryption. This can sometimes be a cheaper way to store data rather than renting space in a data center.
For example, blockchain can be used to securely share electronic health records. Since the data in blockchain is encrypted and private key codes are needed to access the data, these records would be shared among patients and providers safely.
Supply Chain Management
Supply chains are complex and managing them takes hours upon hours of time from businesses and their teams, especially when different links in the chain are in different states or countries.
A blockchain’s immutable record-holding technology solves many issues associated with supply chain management by eliminating the lack of transparency and inefficiencies in payment processes.
One example of this is Walmart using blockchain technology to trace their food sources. Tracing mangos to the source went from longer than six days to 2.2 seconds. As blockchain technology becomes more accessible, more businesses will use it to trace products and keep a secure record of their supply chain.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts can use blockchain technology to ease the headaches associated with managing contracts for businesses. A smart contract is an automated, self-fulfilling contract where payment is only released once it is confirmed that both parties have fulfilled their agreed-upon terms.
The Environmental Impact of Blockchain
Blockchain technologies, particularly those using proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanisms, have been criticized for their significant environmental impact. PoW, the backbone of many popular cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin, requires miners to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and secure the network.
This process consumes vast amounts of electricity due to the need for specialized hardware running continuously at high power. Studies have shown that Bitcoin alone can consume more energy annually than some small countries, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions, especially when powered by fossil fuels.
However, not all blockchain systems are equally energy-intensive. Emerging alternatives, such as proof-of-stake (PoS) mechanisms, significantly reduce energy consumption by eliminating the competitive mining process. Ethereum's transition to PoS in 2022 reportedly cut its energy usage by over 99%.
Additionally, blockchain developers are exploring other sustainable innovations, such as integrating renewable energy sources and optimizing algorithms for efficiency. While blockchain has undeniable potential for innovation, its environmental footprint remains a critical factor for widespread adoption on a global scale, making the ongoing effort for greener solutions an absolute necessity.
Wrapping Up on Blockchain in Business
Like most new technologies, the benefits and pitfalls of blockchain are still being discovered and studied. Innovative businesses are now using it to track their supply chains, share records, and receive payments. As the blockchain becomes more widespread, businesses and consumers all around the world will interact in one way or another with it.
For more information on how Impact can help build out your IT infrastructure, take a few minutes to watch our webinar, A Closer Look at Impact’s Approach to Managed IT.